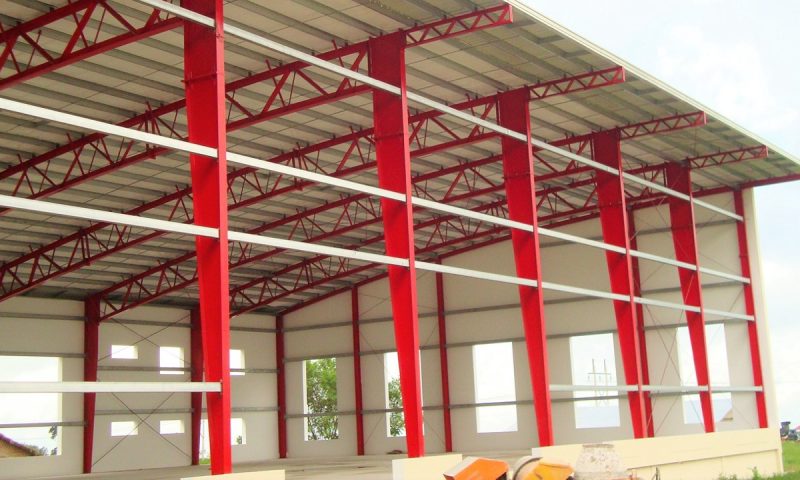
Steel is widely used in the construction industry due to its numerous outstanding advantages. Nowadays, there are various types of steel available on the market, such as hollow steel, steel plates, shaped steel, steel wire rope, etc. Among them, shaped steel is a particularly common and widely applied type. Let’s explore the question “What is shaped steel?”, its different types, and its characteristics with Pebsteel in the following article.
See more: What is Steel Structure? Why should you choose a steel structure?
What is shaped steel?
Shaped steel is processed into shapes such as H, T, U, I, L, etc. Widely used in the construction industry, it plays a crucial role in various specialized fields, including:
• Road and bridge construction
• Shipbuilding industry
• Manufacturing of lifting and transport machinery
• Container frame fabrication
• Industrial factory construction
• Pre-engineered steel buildings
• Piling for foundations
See more: Common Types of Steel Structures in Construction

Types and characteristics of shaped steel
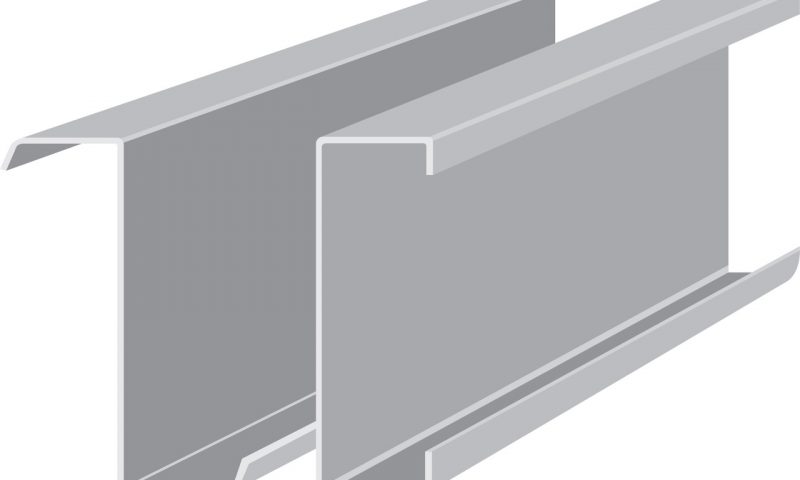
Currently, there are various types of shaped steels available in the market, each applied at specific locations within construction projects, including L-shaped steel, V-shaped steel, U-shaped steel, C-shaped steel, I-shaped steel, and H-shaped steel.
- L-shaped steel: This is a type of shaped steel with an L-shaped cross-sectional area, featuring two perpendicular sides of different lengths. The weight of steel per meter is calculated based on the nominal dimensions and the density of steel at 7.85kg/dm3.
- V-shaped steel: This type of steel has a V-shaped cross-sectional. It is divided into two main forms: common V-shaped steel and hot-dip galvanized V-shaped steel. The latter exhibits better resistance to seawater and certain acids.
- U-shaped steel: This type of steel has a U-shaped form, with diverse dimensions and weights. U-shaped steel is widely used in the construction and engineering fields, serving as a commonly applied steel product.
- C-shaped steel: This steel has a C-shaped cross-section. These days, C-section steel is extensively used in large-scale construction projects and serves as a primary material for manufacturing machinery, household appliances, and furniture.
- I-shaped steel: The height of I-shaped steel, also known as the length between flanges, is considerable compared to the wing part. It is a popular type of steel used in various construction projects due to its distinctive shape.
- H-shaped steel: This is a type of shaped steel product with a cross-sectional area resembling the letter H, featuring two parallel and equal flanges, with the middle portion thinner than the flanges. It is classified into categories such as wide flange, narrow flange, and medium flange. H-shaped steel can be treated with processes such as galvanization, hot-dip coating, or painting to protect the surface.
See more: Structural Steel Properties and Applications
The manufacturing process of shaped steel
The standard manufacturing process of shaped steel consists of 4 main stages: ore processing, creating molten steel stream, ingot casting, and rolling to form the final product.
Ore processing
This is the first step in the steel production process. The raw ore must undergo thorough inspection and evaluation to ensure it meets the required standards before being transferred to the production process. In this way, the quality of the shaped steel produced is guaranteed at its best.
Various types of ore are used in the steel refining process, including iron ore, iron ore pellets, sintered ore, as well as some auxiliary ores such as coke and limestone, etc. The mixture of these raw materials is uniformed fed into the smelting furnace, resulting in a high-strength final product.
See more: Is Steel Structure Better Than Concrete?
Creating molten steel flow
Following the ore processing stage and the subsequent hot smelting process, a molten steel stream is generated. This molten metal stream is transferred to the reheating furnace or electric arc furnace. Here, the molten metal is separated and processed to eliminate impurities, while adjusting the proportion of chemical components. This is an extremely crucial stage, directly impacting the steel grade classification process. Therefore, to meet the standards of the shaped steel, the addition of chemical components at this stage must be carried out with great care and demands high precision.
Ingot casting
To shape the steel, the molten steel flow is directed to the ingot mold. Here, the steel flow is introduced into three basic types of molds: billets, slabs, and Blooms
- Billets: This type of ingot is primarily used to produce rolled steel and ribbed steel bars. The cross-section of this billet is typically 100×100, 125×125, 150×150, and similar dimensions.
- Slabs: This mold is preferred to producing hot-rolled coil steels, steel plates, and various types of shaped steels. Consequently, slabs are more commonly used in steel manufacturing factories.
- Blooms: This is a composite ingot, combining features of both aforementioned ingot types. Blooms are specifically designed for producing construction steels, steel plates, or shaped steels.
Rolling into finished products
The formed ingots from step 3 will be in two states: hot ingot and cold ingot. Both types of ingots are transported to factories for the rolling process to produce finished products.
The hot ingot from the casting line undergoes continuous rolling at high temperatures, producing robust steel products with a bright surface. Product types include U, I, V, H, C-shaped rolled steel, and steel structure bars (with and without ribs).
In the case of cold steel rolling, the steel stream needs to be cooled to the appropriate temperature level. Subsequently, it passes through a descaling line before being fed into the rolling mill through five consecutive stands. The number of rolling passes depends on the thickness of the hot-rolled coil material and the thickness requirements of the final product.
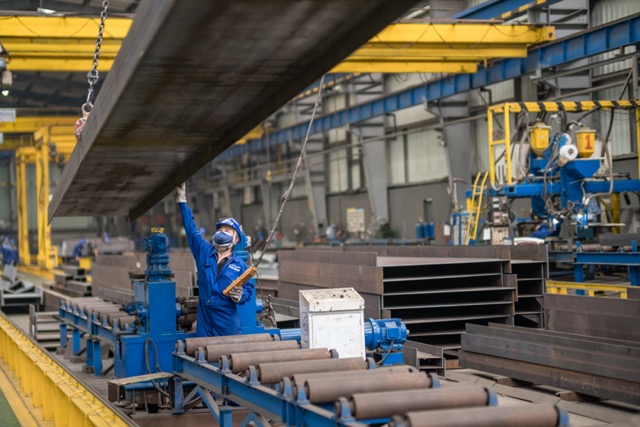

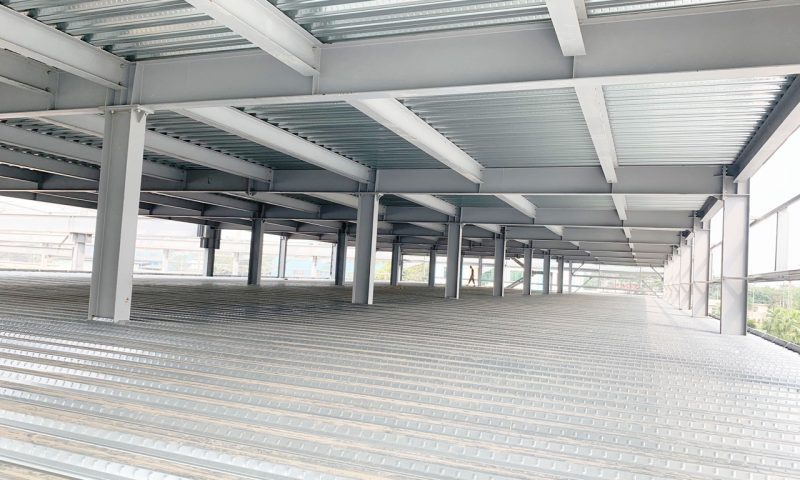
Applications of shaped steel in construction
Shaped steel is a widely trusted and utilized material by investors, primarily due to the exceptional advantages it offers. This type of material is often applied in the construction of bridges, transmission towers, machinery and equipment transportation, as well as in the industrial boiler manufacturing and shipbuilding industries. Specifically, shaped steel is frequently employed in pre-engineered steel buildings. Depending on specific requirements and purposes, investors can choose from various types of shaped steel, suitable for the preferred designs and dimensions.
See more: Advantages of Steel Structure
Conclusion
Above are the details about what shaped steel is, various types of shaped steel, the production process, and their applications in construction. Please contact Pebsteel by phone at +84 908 883531 or by email immediately at Marketing@pebsteel.com.vn if customers require comprehensive solutions for pre-engineered steel buildings and steel structures.







